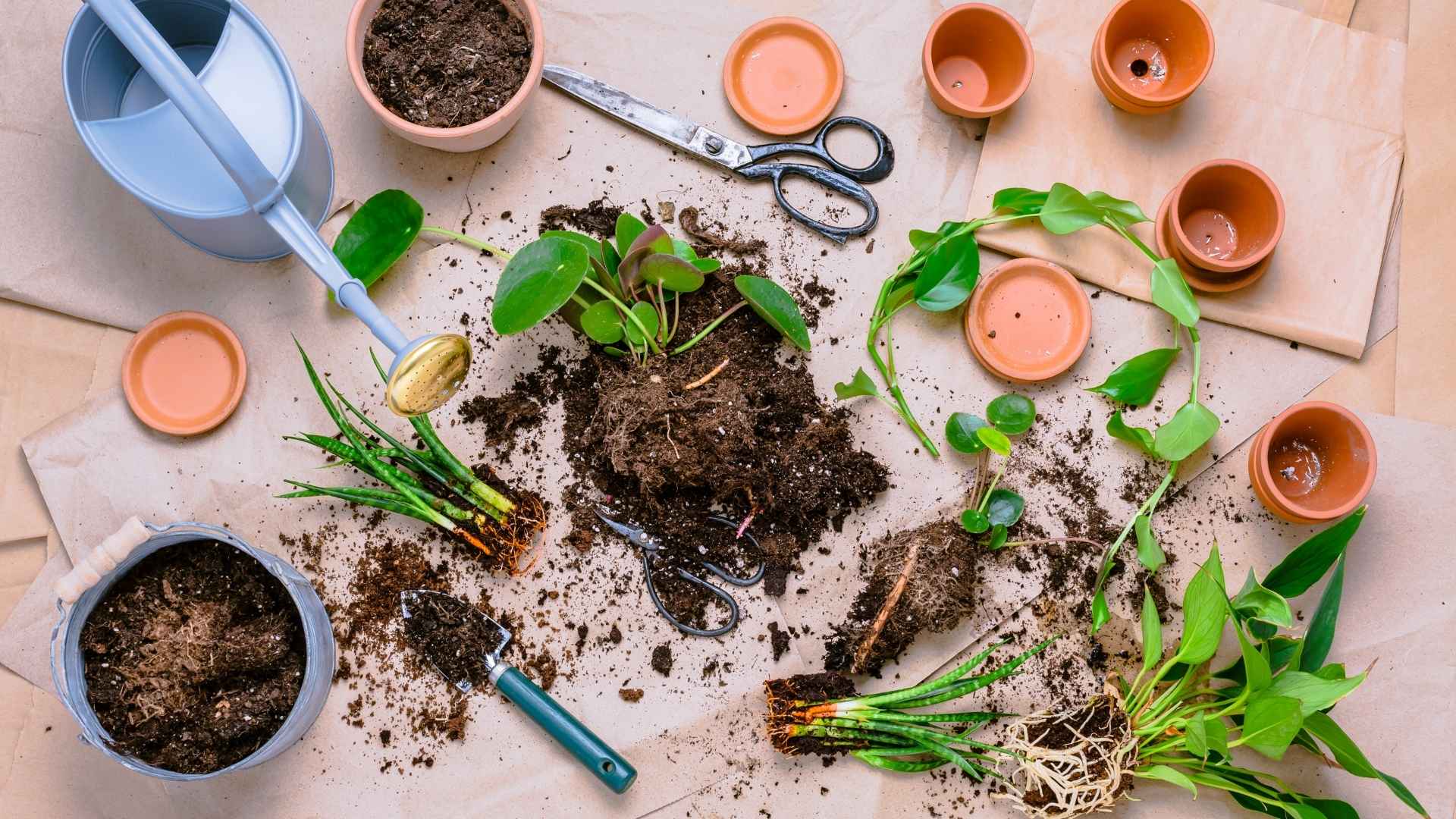

Ultimate Guide to Propagation through Cuttings – 1
Propagation through cuttings is a simple and effective method of plant reproduction where a section of a parent plant is cut and encouraged to grow into a new, independent plant. This method is popular for many plants because it’s fast, inexpensive, and often produces plants identical to the parent.
Types of Cuttings, and General Steps to Propagate via Cuttings
Stem Cuttings: A portion of the stem with nodes (where leaves grow) is taken. Common for plants like roses, mint, and pothos.
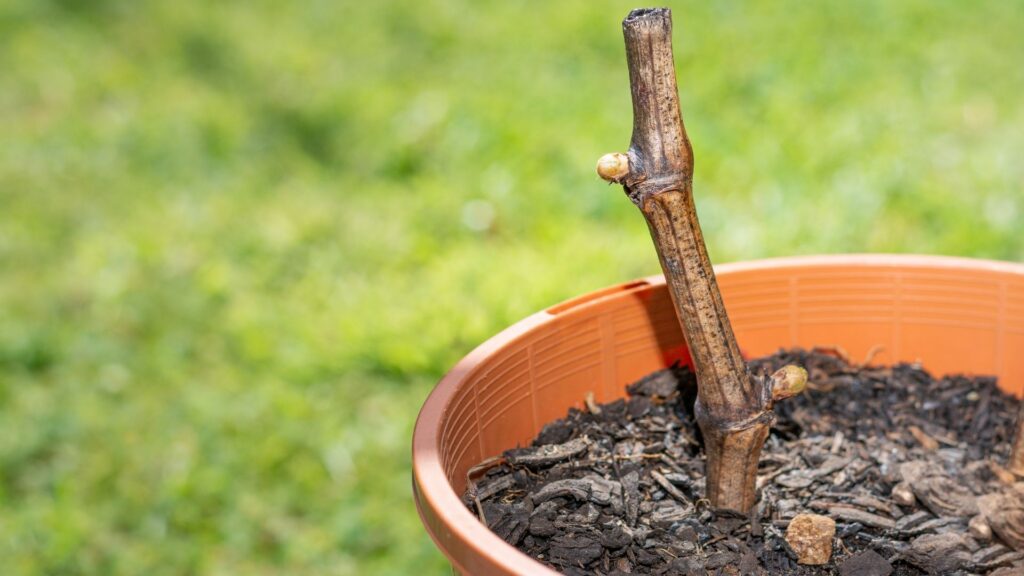

Leaf Cuttings: A single leaf or part of a leaf is used. Suitable for plants like succulents or African violets.
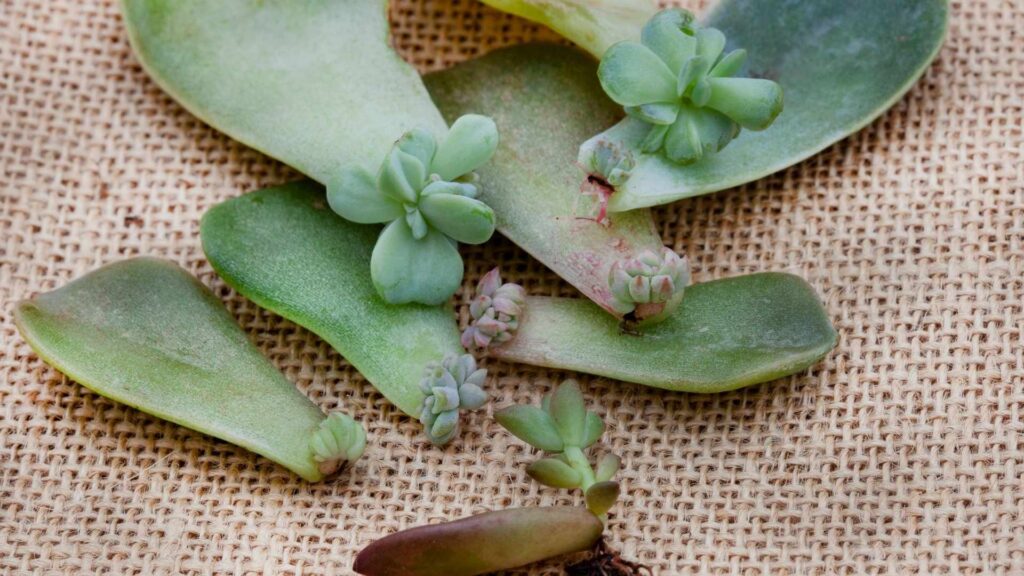

Root Cuttings: Pieces of roots are used, common for plants like horseradish or blackberries.n turpu veya böğürtlen gibi bitkiler için yaygın olan bu yöntemde kök parçaları kullanılır.
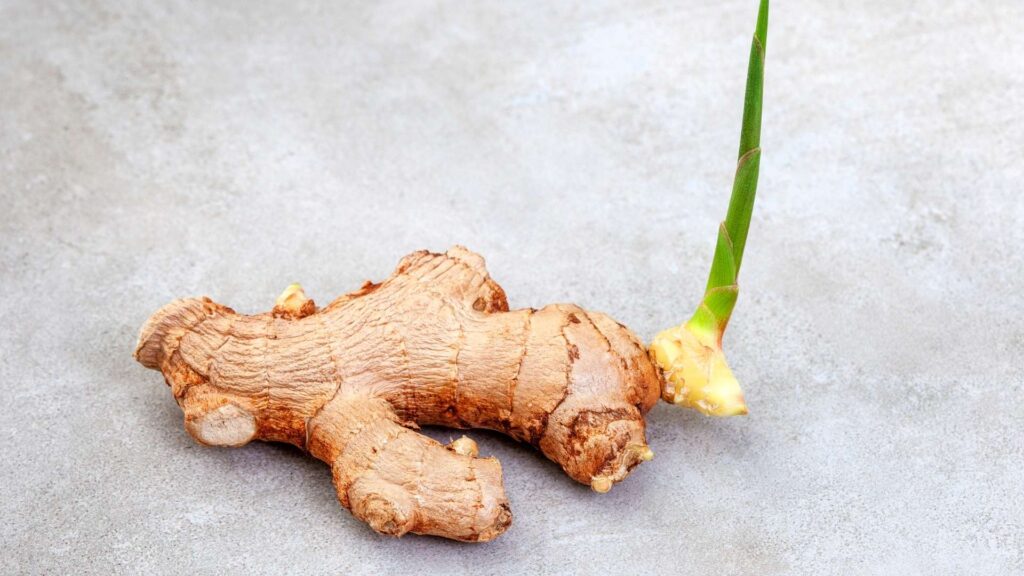

Leaf-Bud Cuttings: A cutting with a single leaf and a bud attached is used.

- Choose a Healthy Plant
Select a disease-free, vigorous parent plant.
- Make the Cut
Use a clean, sharp tool to minimize damage. Cut just below a node (for stem cuttings), as this is where new roots are likely to form.
- Prepare the Cutting
Remove lower leaves to prevent rotting.
Optional: Dip the cut end in rooting hormone to encourage root growth.
- Plant the Cutting
Insert the cut end into a suitable growing medium (e.g., soil, perlite, water, or vermiculite).
Ensure at least one node is buried if it’s a stem cutting.
- Provide Proper Conditions
Maintain high humidity by covering the cutting with a plastic bag or placing it in a humid environment. Place in bright, indirect light. Keep the medium moist but not waterlogged.
- Monitor Growth
Roots usually develop in 1-4 weeks, depending on the plant. Once roots are established, transplant the cutting into a pot or garden bed.
Propagation Methods for Some Favorite Indoor Plants
Here we will provide step by step propagation instructions for some of the favorite house plants in two parts. First part will include favorite plants like Swiss Cheese Plant, Snake Plant, Giant White Bird of Paradise, Prayer Plant, Heartleaf Philodendron.
Instructions for Zamiokulkas, Amazonian Elephant Ear, Ruber Plant, Anthurium Flower, Arrowhead Philodendron will be on our next post.
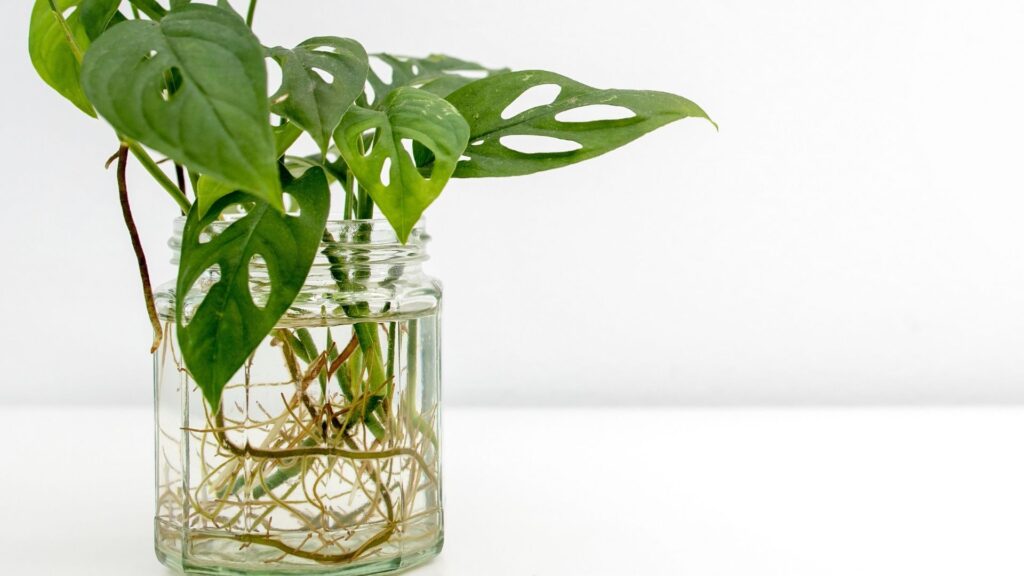
Swiss Cheese Plant – Monstera deliciosa
Choose the Right Cutting
Look for a healthy, mature stem with at least one node. This is the point where the leaf and aerial roots emerge. It’s crucial for root growth. Having aerial roots (brownish roots) also increase the chance of successful propagation.
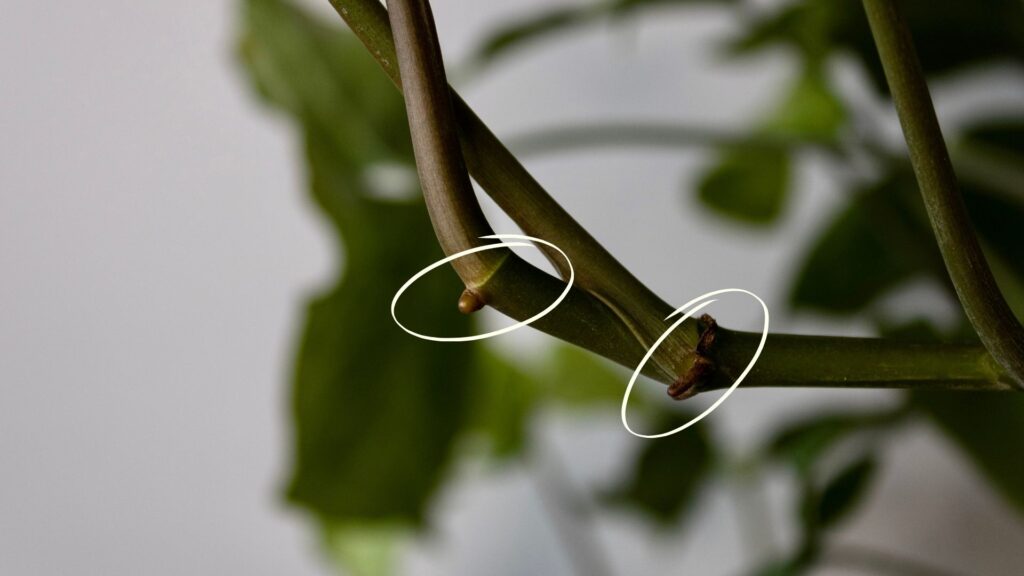

Make the Cut
Cut the stem just below the node. Include at least one leaf above the node. If your cutting has aerial roots, ensure they’re intact, as they will aid in root development.
Decide on Propagation Method
You can propagate Monstera deliciosa in water or soil. Water Propagation is easiest for monitoring root growth. Place the cutting in a clear container filled with clean water. Ensure the node is submerged, but not the leaf. Position the container in bright, indirect light.
Change the water every 5-7 days to prevent stagnation and promote healthy growth.
Roots should develop within 2-6 weeks. Once roots are 2-3 inches long, transplant the cutting into soil. Maintain high humidity (60-70%) to encourage growth. Mist the cutting if the air is dry.
Snake Plant – Dracaena trifasciata
Propagating Snake Plant is straightforward and can be done through leaf cuttings, division, or water propagation.
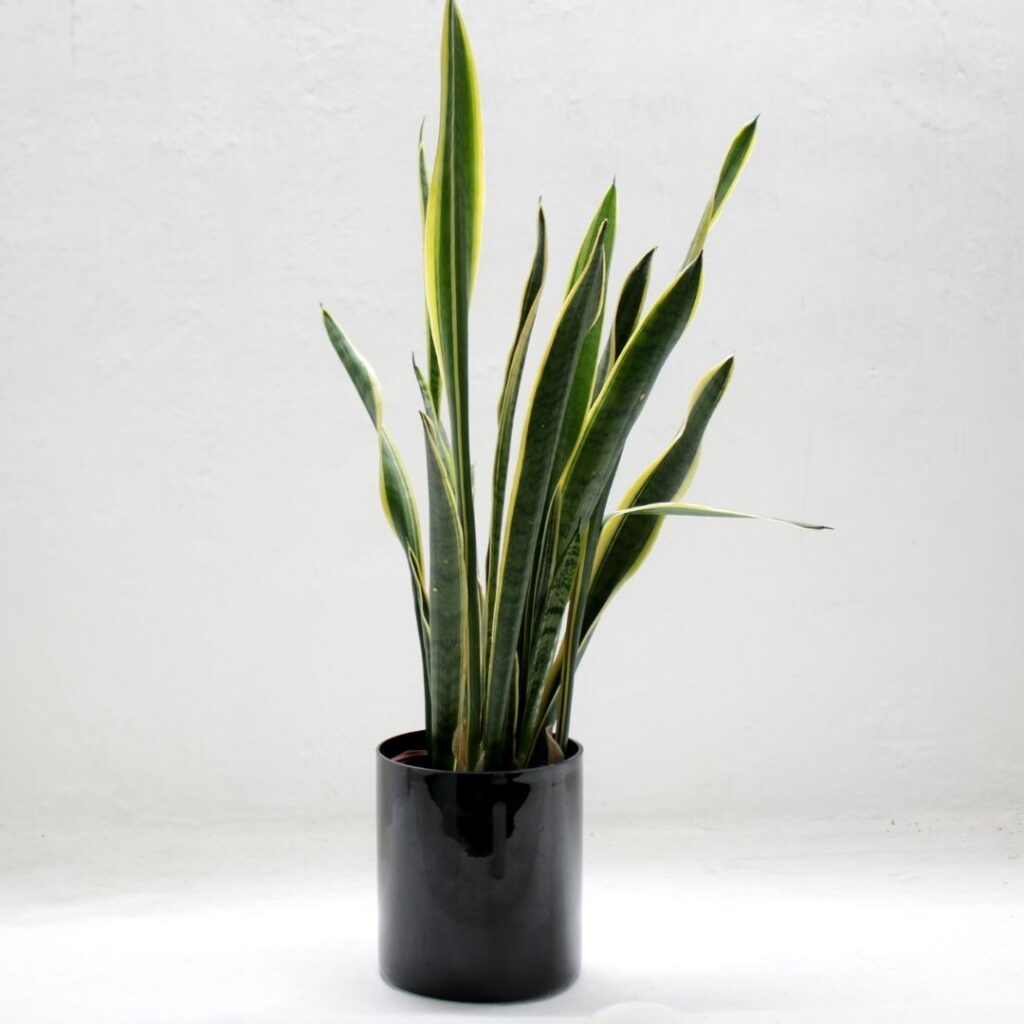

Propagating Through Leaf Cuttings
Choose a mature, healthy leaf without any signs of damage or disease. Cut the leaf into 4–6 inch sections. Ensure you keep track of the bottom end of each section (the part closest to the soil), as planting the wrong end will prevent rooting. Allow the cuttings to dry for 1–2 days to prevent rot. Insert the bottom end of each cutting into moist, well-draining soil (like cactus or succulent mix). Place the pot in bright, indirect light. Water sparingly, letting the soil dry out slightly between waterings. Roots will develop in 4–8 weeks. New growth will eventually emerge from the base.
Propagating Through Division
This is the quickest method and maintains the original plant’s variegation. Gently take out the plant from the pot, being careful not to damage the roots. Identify areas where the plant has naturally divided into clumps with their own root systems. Use your hands or a clean knife to divide the plant into smaller sections, ensuring each has roots attached. Plant each section in its own pot with fresh, well-draining soil. Water lightly to settle the soil.
Propagating Through Water
This method is great for observing root growth. Cut a healthy leaf and cut it into 4–6 inch sections, as with leaf cuttings. Submerge the bottom end of the cutting in a jar of water. Ensure only the bottom portion is submerged to prevent rot. Replace the water every 5–7 days to keep it clean. Roots will appear in 4–8 weeks. Once roots are at least 1–2 inches long, transfer the cutting into soil.
Giant White Bird of Paradise – Strelitzia nicolai
Carefully take the plant out of its pot. If it’s large and difficult to remove, tip the pot sideways and gently work the plant free. Brush off excess soil to expose the roots. Identify sections where the plant has natural divisions (e.g., offshoots or clumps).
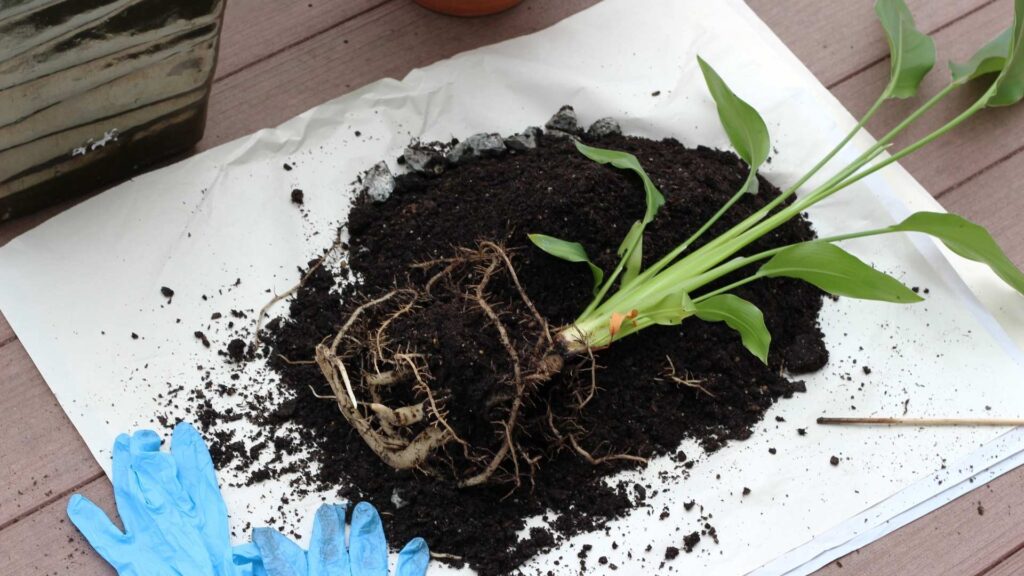

Using your hands or a clean knife, carefully separate the offshoots or clumps. Ensure each division has a stem, leaves, and a good portion of roots attached. Plant each section in its own pot filled with fresh potting mix. Ensure the roots are covered, and the plant is securely positioned. Water lightly to settle the soil around the roots.
Prayer Plant – Maranta leuconeura
Choose the Right Cutting
Choose a stem with at least one node (the bump where leaves and roots grow from). Ensure the stem has a few healthy leaves.
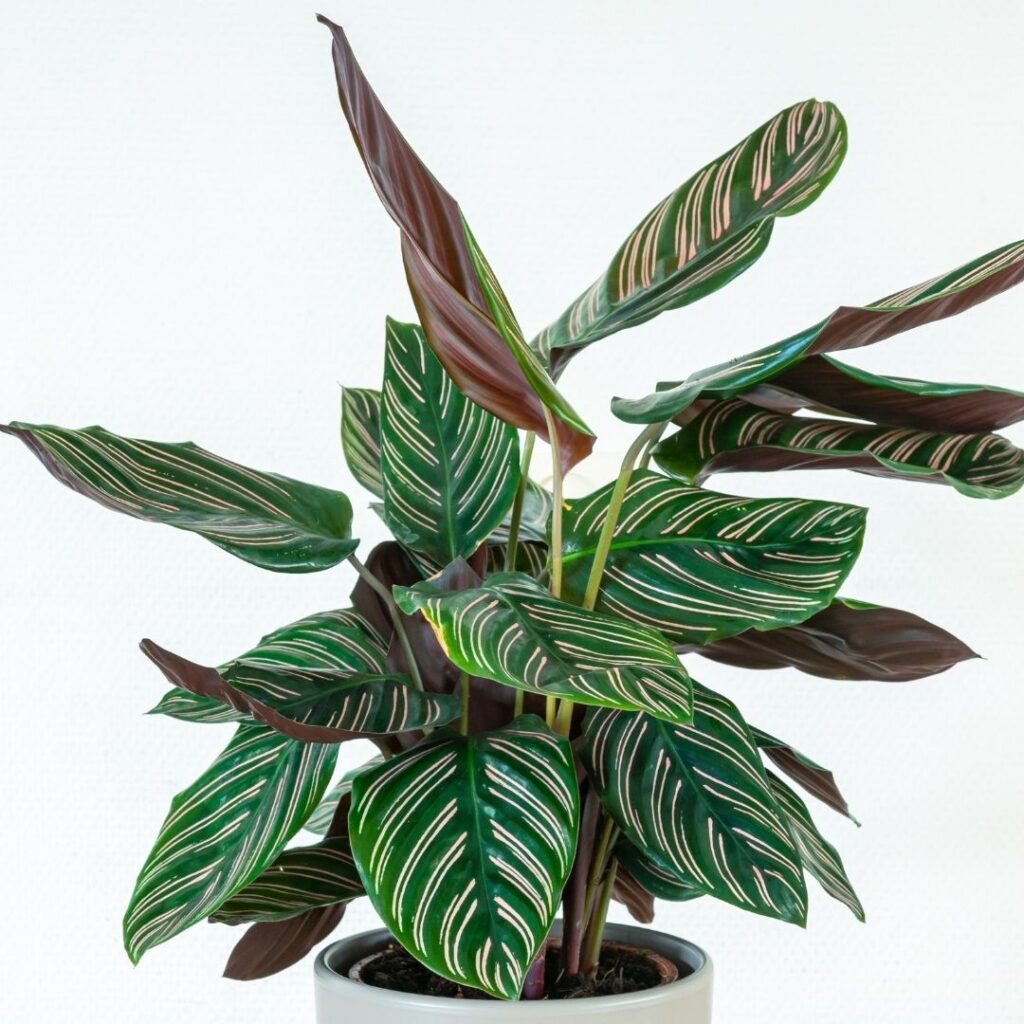

Make the Cut
Use a clean, sharp knife or scissors to cut just below the node. Each cutting should ideally be 4–6 inches long. If there are leaves near the node, gently remove them to avoid rot during propagation.
Decide on Propagation Method
You can propagate prayer plant in water or soil. For water propagation place the cutting in a jar of clean water, ensuring the node is submerged.Keep the jar in bright, indirect light. Change the water every 3–5 days to keep it fresh. Roots will develop in 2–4 weeks. Or plant the cutting in moist, well-draining soil with the node buried. Cover the pot with a plastic bag to create a mini greenhouse and maintain humidity. Place in bright, indirect light.
Heartleaf Philodendron – Philodendron scandens
Choose the Right Cutting
Look for a healthy, mature vine with at least one node. Choose a cutting with 2–4 leaves, as this gives the new plant enough energy to grow.
Make the Cut
Cut the stem just below a node using sterilized scissors or a knife. Each cutting should be 4–6 inches long and include at least one leaf and one node. Remove any leaves close to the node to prevent rotting during propagation.
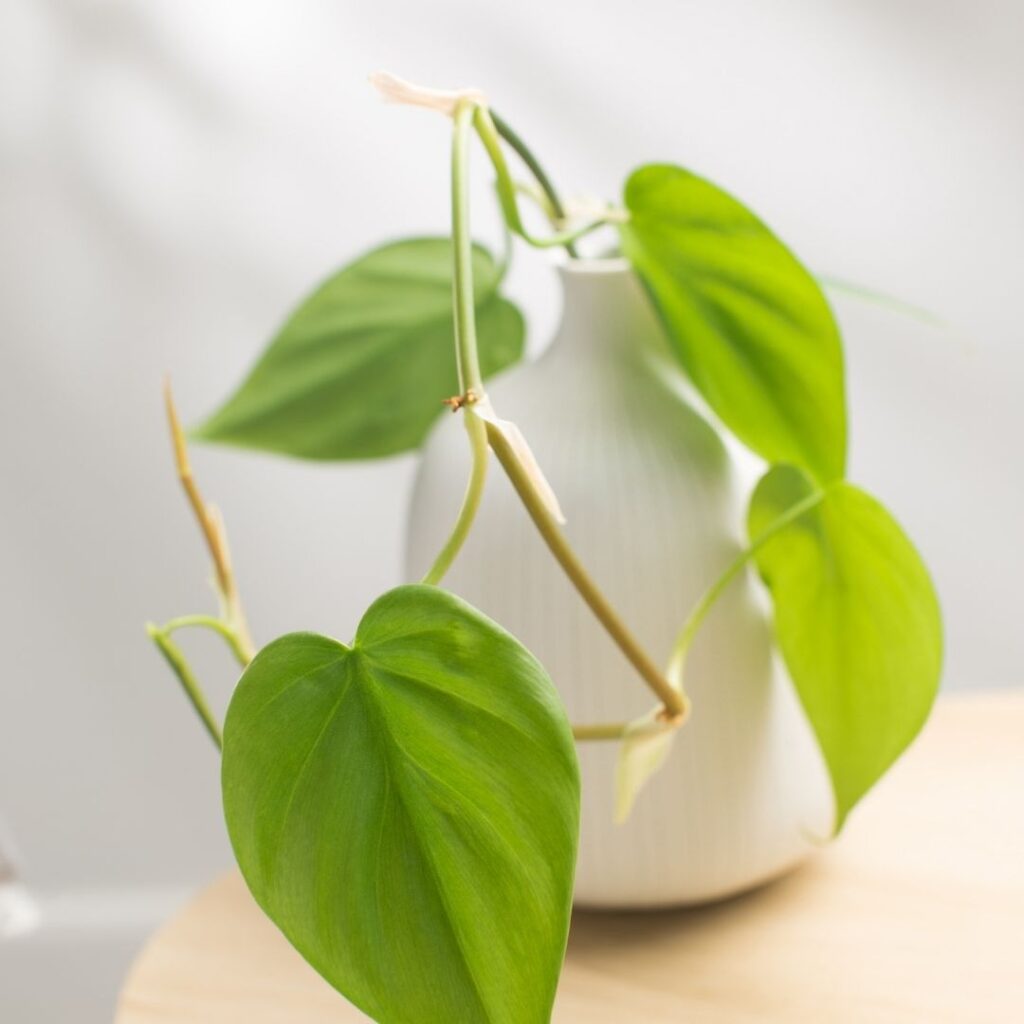

Decide on the Propagation Method
You can propagate plant in water or soil. For water propagation place the cutting in a jar of clean water, ensuring the node is submerged. Keep the jar in bright, indirect light. Change the water every 5–7 days to keep it fresh. Roots will develop in 2–4 weeks. Once roots are 2–3 inches long, transfer the cutting to a pot with soil. Or plant the cutting in moist, well-draining soil with the node buried. Cover the pot with a plastic bag to create a mini greenhouse and maintain humidity. Place in bright, indirect light.
 English
English Türkçe
Türkçe


